In today’s AI-driven landscape, many businesses and individuals are exploring how they can use Generative AI (GenAI) and Machine Learning (ML) to enhance productivity, make data-driven decisions, and solve complex problems. However, it’s easy to overestimate what these technologies can do and expect them to solve all kinds of business challenges. While GenAI and ML share some similarities, they serve distinct purposes, excel in specific tasks, and come with their own set of limitations. Understanding their differences can help you leverage their strengths effectively and ensure that your business gets the most out of AI technology.
This article will explore the core differences between GenAI and ML, break down their respective strengths and weaknesses, and provide the best use cases for each technology to help you maximize their value.
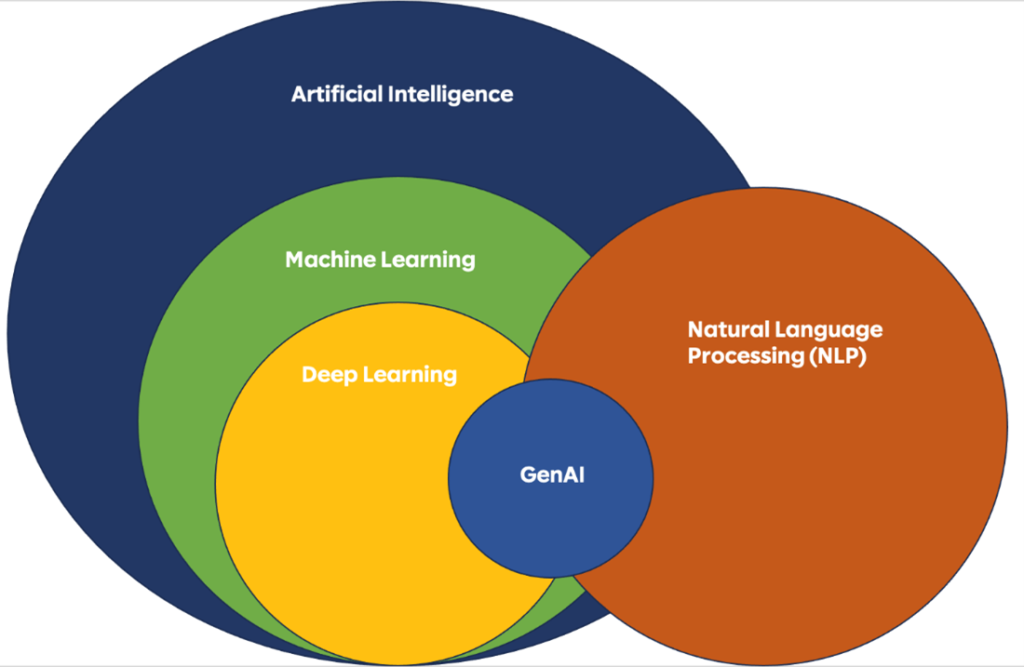
Generative AI vs. Traditional Machine Learning: Key Differences
Although both GenAI and ML are branches of artificial intelligence, they operate quite differently and excel in unique areas.
- Generative AI: Creative Content Generation
- What it is: Generative AI models, like ChatGPT, DALL-E, and others, use large language models (LLMs) or other architectures to create new content, such as text, images, music, and even code.
- Primary Use: GenAI is designed to mimic human creativity, producing content that is often original in tone, style, and subject matter. It’s highly effective at natural language processing and generating human-like responses.
- Limitations: GenAI is not well-suited for complex numerical calculations or precise quantitative predictions. Its “knowledge” is largely based on data patterns rather than real-time or numerical data analysis, so it may lack accuracy in number-centric tasks.
- Traditional Machine Learning: Data-Driven Predictions
- What it is: Machine Learning models analyze and learn from historical data to make predictions or decisions based on statistical methods. ML is ideal for quantitative tasks, such as classification, regression, clustering, and anomaly detection.
- Primary Use: ML models are ideal for forecasting, trend analysis, fraud detection, and other tasks where precise predictions from structured data are needed.
- Limitations: ML lacks the flexibility and creativity of GenAI, making it less effective for tasks that require human-like content creation or conversational responses.
Understanding these core distinctions helps clarify when each technology should be used.
Strengths and Weaknesses: GenAI and Machine Learning
Let’s delve into the strengths and weaknesses of both GenAI and ML to better understand their optimal use cases.
Generative AI Strengths
- Creativity and Content Generation: GenAI excels in producing human-like language, generating images, and drafting text that resembles human thought and style.
- Natural Language Processing: Ideal for chatbots, customer support, and content creation, GenAI understands context and can simulate human interactions effectively.
- Versatility in Content Forms: GenAI can create varied forms of content, from visual designs to social media posts, providing a broad range of applications for creative industries.
Generative AI Weaknesses
- Accuracy in Calculations: GenAI struggles with numerical precision, as it’s not specifically designed to handle calculations or data analysis.
- Dependence on Pre-trained Data: Since GenAI models rely on pre-trained data, they lack up-to-date information and can perpetuate inaccuracies if the training data is outdated or biased.
- Limited Predictive Capabilities: GenAI can create text and images but doesn’t predict trends or future data as accurately as ML, making it less suitable for forecasting.
Machine Learning Strengths
- Predictive Power: ML’s ability to forecast based on historical data makes it ideal for sales projections, inventory management, and customer behavior analysis.
- Data Pattern Recognition: ML is highly effective at identifying patterns in structured data, leading to accurate predictions and classification tasks.
- Quantitative Precision: ML can handle complex calculations and is well-suited for fields requiring numerical analysis, like finance, logistics, and scientific research.
Machine Learning Weaknesses
- Limited Creativity: ML’s outputs are constrained by the structured data it analyzes, making it less effective in areas requiring creativity, tone variation, or conversational understanding.
- Complex Setup and Training Needs: ML models require curated datasets, feature engineering, and ongoing adjustments, which can be resource-intensive.
- Lower Flexibility for Open-Ended Tasks: ML models are specialized and work best with specific, structured data. They’re not ideal for open-ended, creative tasks that GenAI handles well.
Best Use Cases for Generative AI
Generative AI’s unique capabilities make it ideal for several key applications in content creation and customer interaction. Here are some practical ways to utilize GenAI effectively.
1. Content Creation and Marketing
GenAI is a powerful tool for producing marketing content quickly and consistently. It can draft blog posts, social media captions, newsletters, and product descriptions in a matter of minutes, saving time and reducing costs for marketing teams. For example, small businesses can leverage GenAI tools like ChatGPT to generate high-quality text for social media posts, tailored emails, or brand stories that resonate with their audience.
2. Customer Service and Support Automation
Chatbots powered by GenAI can handle basic customer queries, such as FAQs, order updates, and service troubleshooting. By providing 24/7 customer support, GenAI chatbots reduce workload on customer service teams, allowing staff to focus on complex issues. These AI-driven responses help improve response times and customer satisfaction, especially in sectors like retail, hospitality, and eCommerce.
3. Creative Design Assistance
GenAI models like DALL-E can help designers generate ideas for visual content, from logo concepts to advertisement graphics. While a human designer ultimately refines the concept, GenAI offers initial inspiration that speeds up the creative process. This is especially helpful for smaller businesses without dedicated design teams.
4. Language Translation and Localization
GenAI supports natural language translation, allowing businesses to offer localized content for diverse markets. This is especially valuable for SMEs looking to expand internationally, as they can quickly translate promotional content, product descriptions, and customer communications with relative ease and consistency.
Best Use Cases for Machine Learning
Machine Learning’s precision and predictive capabilities make it indispensable for tasks that rely on historical data, structured patterns, and quantitative analysis. Here are the top applications.
1. Sales Forecasting and Inventory Management
ML models analyze sales data to predict future demand, helping businesses stock inventory efficiently and reduce waste. This is invaluable for retail, manufacturing, and logistics, where inventory accuracy impacts profits. For example, ML-driven forecasting can help a grocery store predict demand for certain products during peak seasons, ensuring they stock the right amounts without overcommitting.
2. Customer Behavior Analysis and Segmentation
ML models analyze customer data to identify segments based on purchasing behaviors, preferences, and demographics. By understanding different customer segments, businesses can personalize marketing efforts and improve customer loyalty. An online retailer, for example, can use ML algorithms to recommend products based on past purchases, increasing cross-selling opportunities.
3. Fraud Detection and Risk Management
In sectors like finance and insurance, ML models detect anomalies that indicate potential fraud. ML algorithms monitor transactions, flag unusual behavior, and help businesses mitigate risks early. For instance, a credit card company might use ML to detect suspicious transactions, protecting customers and reducing financial loss.
4. Predictive Maintenance for Equipment
For businesses that rely on machinery, ML models predict equipment failure based on usage patterns and maintenance history. Predictive maintenance minimizes downtime and reduces repair costs, making it highly valuable in manufacturing, logistics, and any field that relies on equipment performance.
5. Financial Forecasting and Budgeting
ML models process historical financial data to generate accurate forecasts, enabling businesses to budget effectively. By identifying trends and predicting revenue, ML supports more informed decision-making. This is critical for companies in finance, real estate, and other sectors where financial forecasting is essential for planning and growth.
Choosing the Right Approach: When to Use GenAI vs. Machine Learning
The choice between GenAI and ML often depends on the specific business need:
- Use GenAI for Creative Content, Customer Interaction, and Language-Based Tasks. GenAI is ideal for tasks that require human-like conversation, written content creation, or initial design ideas. This includes marketing, customer support, and social media management.
- Use ML for Predictive, Quantitative, and Data-Driven Tasks. ML excels in structured environments where historical data patterns lead to actionable insights, such as sales forecasting, risk analysis, and customer segmentation.
To maximize the potential of both technologies, some businesses integrate them. For example, a retail business could use ML to predict customer trends and then employ GenAI to create personalized marketing content for each segment. This hybrid approach combines the best of both worlds, enhancing decision-making and customer engagement.
Conclusion
Generative AI and Machine Learning each bring unique capabilities to the table, offering specific solutions that address different aspects of business operations. GenAI shines in creative and conversational applications, enhancing marketing, customer service, and content creation, while Machine Learning provides precise, data-driven insights for forecasting, risk management, and quantitative analysis.
Understanding these strengths and applying each technology where it’s most effective can help businesses increase productivity, save costs, and gain a competitive edge. Instead of expecting either AI model to be a catch-all solution, leveraging the best of GenAI and ML in the right contexts can lead to transformative results. By staying informed and strategically deploying each type of AI, businesses can fully harness the power of artificial intelligence and maintain a balanced approach to technology adoption.